Inverse electron demand Diels–Alder – add electron density to the dienophile (raise HOMO) and remove electron density from the diene (lower LUMO). The types of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups are the same as above. 13.3: Diels–Alder reaction is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by
Regiochemistry of the Diels–Alder Reaction with Practice Problems – Chemistry Steps
Find the product of the given Diels–Alder reaction. Draw the product(s) of the given Diels–Alder reaction, and indicate the stereochemistry. Find the product that would be formed in the given Diels–Alder reaction. Provide the product of this Diels Alder reaction: Predict the major product for the following Diels–Alder reaction.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Step 2: Push the Electrons. Now it’s time to use the curved arrows to push electrons where they need to go in the reaction. Start by creating a new bond using the pi electrons from the diene. Then

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Solved Draw the correct product for the following | Chegg.com Acrylic acid’s methyl ester is methyl acrylate. In the Diels–Alder reaction, it is a very useful organic compound. We need one diene and one dienophile for the Diels–Alder reaction. It is an excellent dienophile due to the electron-withdrawing group attached to it, which speeds up the Diels–Alder reaction.
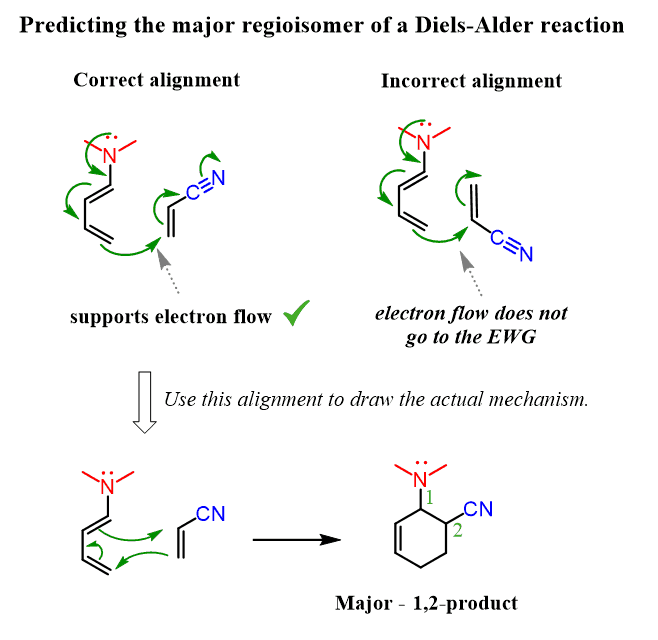
Source Image: chemistrysteps.com
Download Image
Draw The Correct Product For The Given Diels Alder Reaction
Acrylic acid’s methyl ester is methyl acrylate. In the Diels–Alder reaction, it is a very useful organic compound. We need one diene and one dienophile for the Diels–Alder reaction. It is an excellent dienophile due to the electron-withdrawing group attached to it, which speeds up the Diels–Alder reaction. 7.4K Learn about the Diels–Alder reaction. Understand the mechanism of Diels–Alder reaction, the stereochemistry of the reactants and products, and see examples. Related to this
Regiochemistry of the Diels–Alder Reaction with Practice Problems – Chemistry Steps
The Diels–Alder reaction is a concerted reaction, this means it occurs in only one step. Moreover, all of the atoms that are participating in the reaction form bonds simultaneously. Secondly, Diels–Alder reactions are stereospecific.This means that the substituents attached to the both the diene and the dienophile retain their stereochemistry The Diels-Alder Reaction | MendelSet
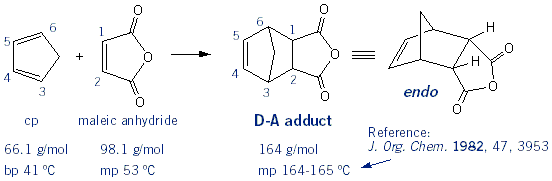
Source Image: mendelset.com
Download Image
Open Flask: 2018 The Diels–Alder reaction is a concerted reaction, this means it occurs in only one step. Moreover, all of the atoms that are participating in the reaction form bonds simultaneously. Secondly, Diels–Alder reactions are stereospecific.This means that the substituents attached to the both the diene and the dienophile retain their stereochemistry

Source Image: openflask.blogspot.com
Download Image
Regiochemistry of the Diels–Alder Reaction with Practice Problems – Chemistry Steps Inverse electron demand Diels–Alder – add electron density to the dienophile (raise HOMO) and remove electron density from the diene (lower LUMO). The types of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups are the same as above. 13.3: Diels–Alder reaction is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by
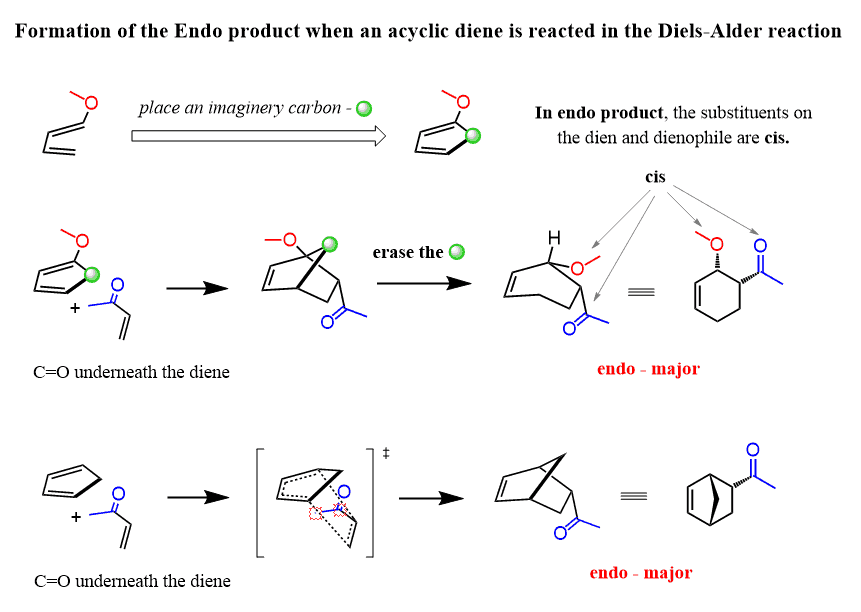
Source Image: chemistrysteps.com
Download Image
Solved Draw the correct product for the following | Chegg.com Step 2: Push the Electrons. Now it’s time to use the curved arrows to push electrons where they need to go in the reaction. Start by creating a new bond using the pi electrons from the diene. Then
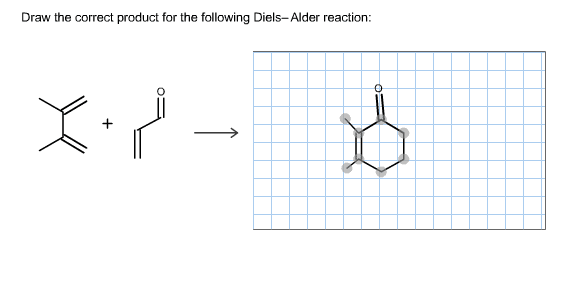
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
OneClass: Draw the product(s) of the Diels-Alder reaction of 1,3-butadiene with c/s-1,2-dibromoethen… The Diels–Alder cycloaddition reaction occurs most rapidly if the alkene component, called the dienophile (“diene lover”), has an electron-withdrawing substituent group. Thus, ethylene itself reacts sluggishly, but propenal, ethyl propenoate, maleic anhydride, benzoquinone, propenenitrile, and similar compounds are highly reactive.

Source Image: oneclass.com
Download Image
Solved Deconstruct the given Diels-Alder adduct. Draw the | Chegg.com Acrylic acid’s methyl ester is methyl acrylate. In the Diels–Alder reaction, it is a very useful organic compound. We need one diene and one dienophile for the Diels–Alder reaction. It is an excellent dienophile due to the electron-withdrawing group attached to it, which speeds up the Diels–Alder reaction.
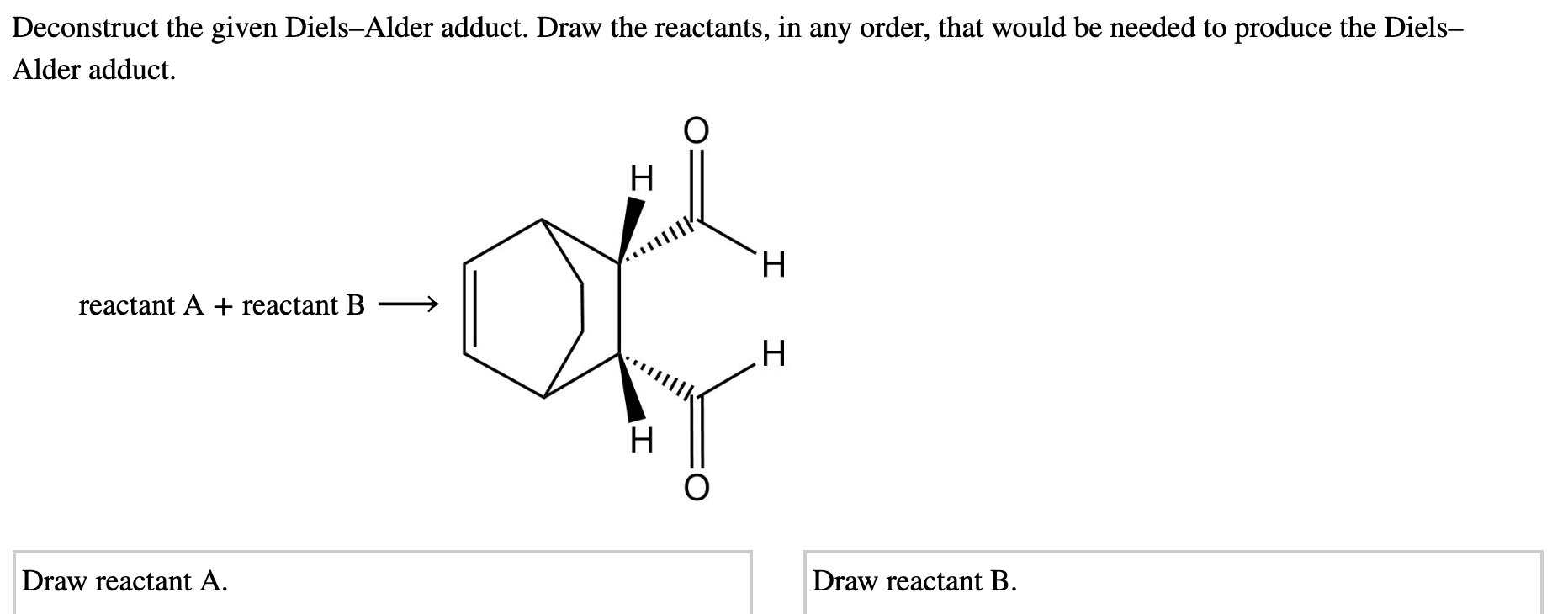
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
A Level H2 Chemistry Tuition and notes Singapore 7.4K Learn about the Diels–Alder reaction. Understand the mechanism of Diels–Alder reaction, the stereochemistry of the reactants and products, and see examples. Related to this

Source Image: alevelchemistrysg.com
Download Image
Open Flask: 2018
A Level H2 Chemistry Tuition and notes Singapore Find the product of the given Diels–Alder reaction. Draw the product(s) of the given Diels–Alder reaction, and indicate the stereochemistry. Find the product that would be formed in the given Diels–Alder reaction. Provide the product of this Diels Alder reaction: Predict the major product for the following Diels–Alder reaction.
Solved Draw the correct product for the following | Chegg.com Solved Deconstruct the given Diels-Alder adduct. Draw the | Chegg.com The Diels–Alder cycloaddition reaction occurs most rapidly if the alkene component, called the dienophile (“diene lover”), has an electron-withdrawing substituent group. Thus, ethylene itself reacts sluggishly, but propenal, ethyl propenoate, maleic anhydride, benzoquinone, propenenitrile, and similar compounds are highly reactive.